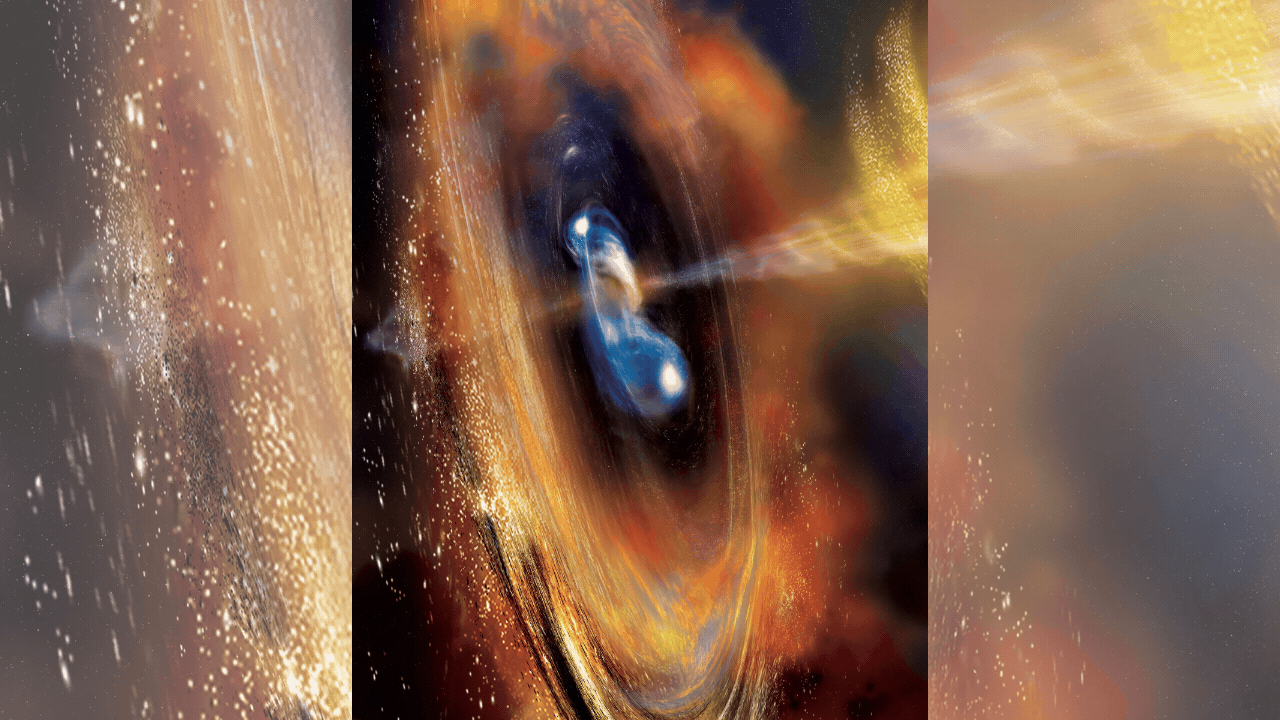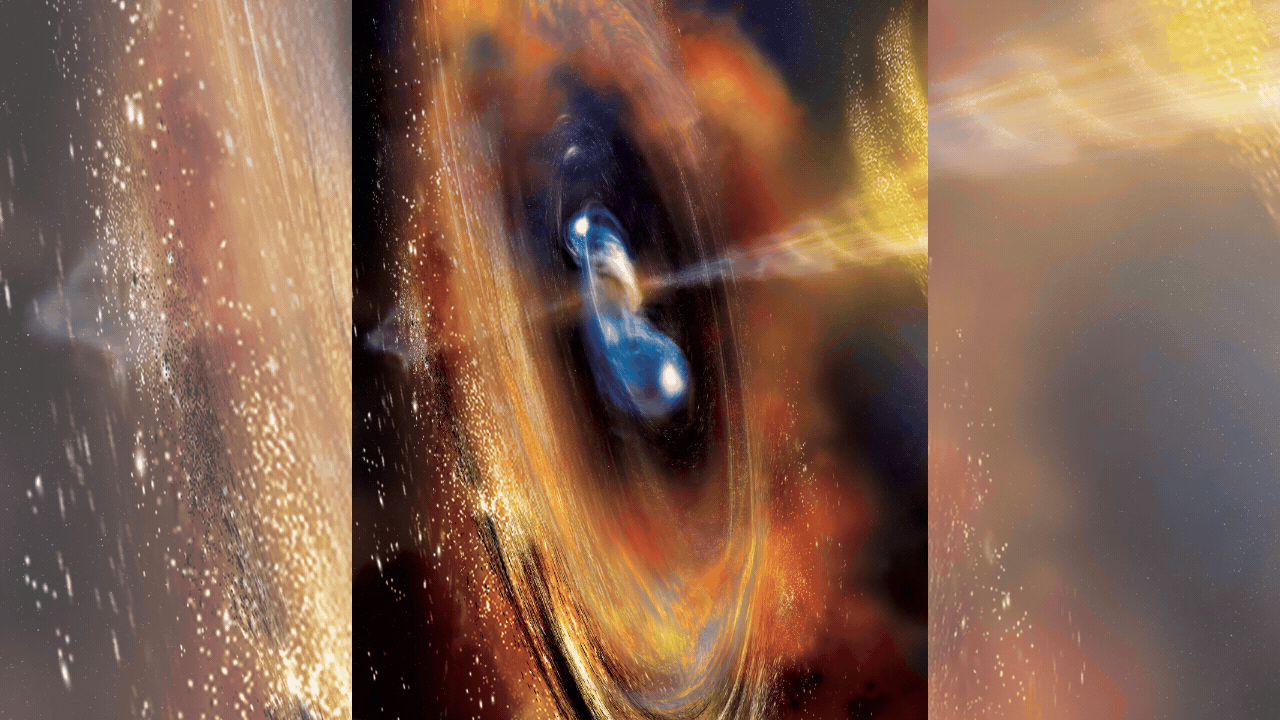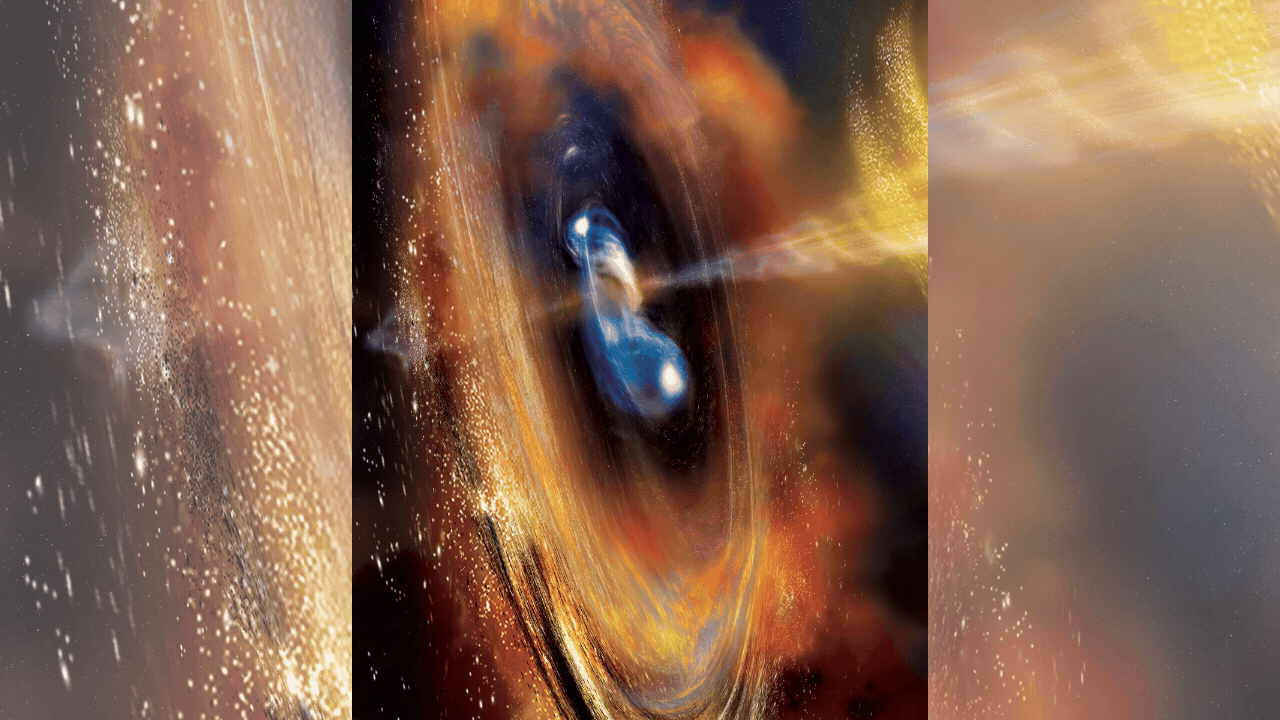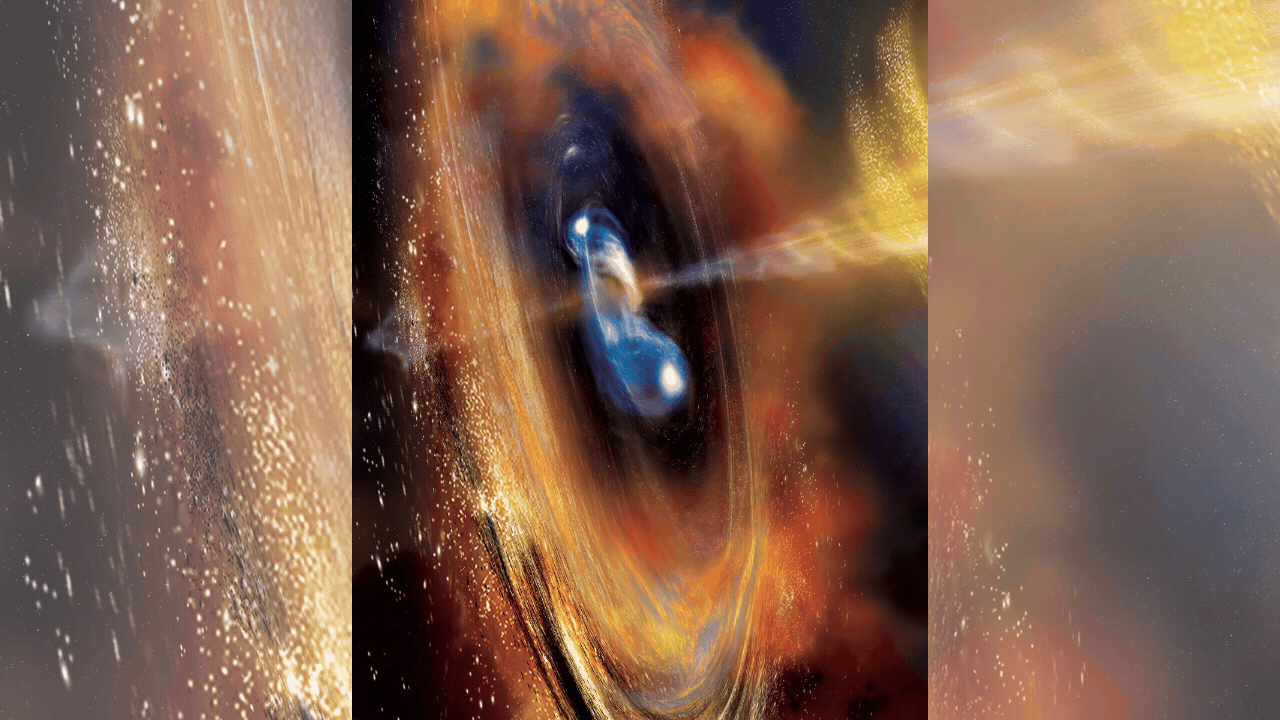[ad_1]
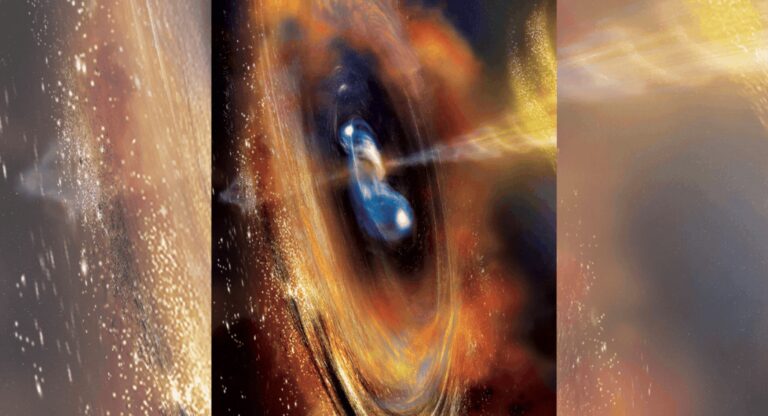
NEW DELHI: A Long March 2-C rocket carrying the French-Chinese satellite Space Variable Objects Monitor (SVOM) successfully lifted off from southwestern China on Saturday to explore the universe’s most powerful explosions, gamma-ray bursts.
The SVOM satellite, weighing 930 kilograms and equipped with instruments from both countries, aims to detect and study gamma-ray bursts, which are extremely bright cosmic events resulting from massive star explosions or compact star mergers.The launch took place at around 3:00 pm (0700 GMT) from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center, as witnessed by AFP journalists.
The satellite’s primary mission is to capture gamma-ray bursts, providing valuable data on the universe’s history and evolution. Gamma-ray bursts emit energy comparable to over a billion billion suns and carry information about the cosmic environments they traverse. This data is critical for understanding the formation and transformation of galaxies and gas clouds.
“Observing them is like looking back in time, as the light from these objects takes a long time to reach us,” explained Ore Gottlieb, an astrophysicist at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Astrophysics in New York.
SVOM aims to uncover several mysteries associated with gamma-ray bursts, including detecting the most distant and earliest bursts in the universe’s history. “SVOM has the potential to unravel several mysteries in the field of (gamma-ray bursts), including detecting the most distant GRBs in the universe, which correspond to the earliest GRBs,” Gottlieb added.
This project marks a cooperation between the French and Chinese space agencies, along with other scientific and technical organizations from both nations. Despite limited space collaboration between China and Western countries due to US restrictions on technology transfer, this partnership exemplifies successful international scientific cooperation.
“US concerns on technology transfer have inhibited US allies from collaborating with the Chinese very much, but it does happen occasionally,” said Jonathan McDowell, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics.
Earlier in 2018, China and France launched CFOSAT, an oceanographic satellite, and several European nations have participated in China’s Chang’e lunar exploration missions. While such collaborations are rare, they highlight the growing scientific cooperation between China and Western countries.
Gamma-ray bursts are brief and intense, presenting a challenge for data collection. The SVOM satellite will orbit 625 kilometers above Earth and send real-time data to ground observatories. Upon detecting a burst, SVOM will alert a team of scientists, who have only five minutes to activate a network of telescopes to capture detailed observations.
Frederic Daigne, an astrophysicist at the Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris, emphasized the importance of studying gamma-ray bursts: “We are… interested in gamma-ray bursts for their own sake, because they are very extreme cosmic explosions which allow us to better understand the death of certain stars.”
The data gathered will help test the laws of physics under conditions that cannot be replicated on Earth and provide insights into the dynamics of the universe.
The SVOM satellite, weighing 930 kilograms and equipped with instruments from both countries, aims to detect and study gamma-ray bursts, which are extremely bright cosmic events resulting from massive star explosions or compact star mergers.The launch took place at around 3:00 pm (0700 GMT) from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center, as witnessed by AFP journalists.
The satellite’s primary mission is to capture gamma-ray bursts, providing valuable data on the universe’s history and evolution. Gamma-ray bursts emit energy comparable to over a billion billion suns and carry information about the cosmic environments they traverse. This data is critical for understanding the formation and transformation of galaxies and gas clouds.
“Observing them is like looking back in time, as the light from these objects takes a long time to reach us,” explained Ore Gottlieb, an astrophysicist at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Astrophysics in New York.
SVOM aims to uncover several mysteries associated with gamma-ray bursts, including detecting the most distant and earliest bursts in the universe’s history. “SVOM has the potential to unravel several mysteries in the field of (gamma-ray bursts), including detecting the most distant GRBs in the universe, which correspond to the earliest GRBs,” Gottlieb added.
This project marks a cooperation between the French and Chinese space agencies, along with other scientific and technical organizations from both nations. Despite limited space collaboration between China and Western countries due to US restrictions on technology transfer, this partnership exemplifies successful international scientific cooperation.
“US concerns on technology transfer have inhibited US allies from collaborating with the Chinese very much, but it does happen occasionally,” said Jonathan McDowell, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics.
Earlier in 2018, China and France launched CFOSAT, an oceanographic satellite, and several European nations have participated in China’s Chang’e lunar exploration missions. While such collaborations are rare, they highlight the growing scientific cooperation between China and Western countries.
Gamma-ray bursts are brief and intense, presenting a challenge for data collection. The SVOM satellite will orbit 625 kilometers above Earth and send real-time data to ground observatories. Upon detecting a burst, SVOM will alert a team of scientists, who have only five minutes to activate a network of telescopes to capture detailed observations.
Frederic Daigne, an astrophysicist at the Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris, emphasized the importance of studying gamma-ray bursts: “We are… interested in gamma-ray bursts for their own sake, because they are very extreme cosmic explosions which allow us to better understand the death of certain stars.”
The data gathered will help test the laws of physics under conditions that cannot be replicated on Earth and provide insights into the dynamics of the universe.
[ad_2]